| [1] 赵景新,刘惠亮,赵凤琴.药物洗脱支架的研究进展[J].中国实用医药,2007,2(31):136-138.
[2] Serruys PW,Ormiston JA,Onuma Y,et al. A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system (ABSORB): 2-year outcomes and results from multiple imaging methods. Lancet. 2009;373(9667):897-910.
[3] Ormiston JA, Serruys PW, Regar E,et al. A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system for patients with single de-novo coronary artery lesions (ABSORB): a prospective open-label trial.Lancet.2008;371(9616):899-907.
[4] Cutlip DE,Windecker S,Mehran R, et al.Clinical end points in coronary stent trials: a case for standardized definitions. Circulation.2007;115(17):2344-2351.
[5] CrossRef Onuma Y,Serruys PW,Ormiston JA,et al.Three-year results of clinical follow-up after a bioresorbable everolimus-eluting scaffold in patients with de novo coronary artery disease: the ABSORB trial. EuroIntervention. 2010;6(4): 447-453.
[6] Joner M,Finn AV,Farb A,et al.Pathology of drug-eluting stents in humans:delayed healing and late thrombotic risk.J Am Coll Cardiol.2006;48:193-202.
[7] Onuma Y,Serruys PW,Gomez J,et al.Comparison of in vivo acute stent recoil between the bioresorbable everolimus-eluting coronary scaffolds(revision 1.0 and 1.1) and the metallic everolimus-eluting stent.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2011;78:3-12.
[8] Ormiston JA,Serruys PW,Onuma Y,et al.First Serial assessment at 6 months and 2 years of the second generation of absorb everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold:a multi-imaging modality study.Circ Cardiovasc Interv.2012;5:620-632.
[9] Ambrosio AM,Sahota JS,Khan Y,et al.A novel amorphous calcium phosphate polymer ceramic for bone repair: I. Synthesis and characterization.J Biomed Mater Res. 2001; 58(3):295-301.
[10] Linhart W,Peters F,Lehmann W,et al.Biologically and chemically optimized composites of carbonated apatite and polyglycolide as bone substitution materials. J Biomed Mater Res.2001;54(2):62-171.
[11] LanZ,LyuY,Xiao J,et al.Novel biodegradable drug-eluting stent composed of poly-L-lactic acid and amorphous calcium phosphate nanoparticles demonstrates improved structural and functional performance for coronary artery disease. J Biomed Nanotechnol.2014;10(7):1-11.
[12] Farb A,Heller PF,Shroff S,et al.Pathological analysis of local delivery of paclitaxel via a polymer-coated stent. Circulation. 2001;104(4):473-479.
[13] Giannakakou P,Robey R,Fojo T,et al.Low concentrations of paclitaxel induce cell type-dependent p53,p21 and G1/G2 arrest instead of mitotic arrest:molecular determinants of paclitaxel- induced cytotoxicity. Oncogene. 2001;20(29): 3806-3813.
[14] Colombo A,Drzewiecki J,Banning A,et al.Randmized study to assess the effectiveness of slow- and moderate-release polymer-based paclitaxel-eluting stents for conronary artery lesions.Circulation.2003;108:788-794.
[15] Liistro F,Stankovic G,Di Mario C,et al.First clinical experience with a paclitaxel derivate-eluting polymer stent system implantation for instent restenosis:immediate and long-term clinical and angiographic outcome. Circulation. 2002;105: 1883-1886.
[16] Kaushal V,Schlichter LC.Mechanisms of microglia-mediated neurotoxicity in a new model of the stroke penumbra.J Neurosci.2008;28(9):2221-2230.
[17] Donato AJ,Black AD,Jablonski KL,et al. Aging is associated with greater nuclear NF κB, reduced Iκ Bα , and increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines in vascular endothelial cells ofhealthy humans. Aging Cell. 2008;7(6):805-812.
[18] 王新,李文杰.NF-κB与动脉粥样硬化的相关性及中药的干预作用[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2009,11(3):55-56. |
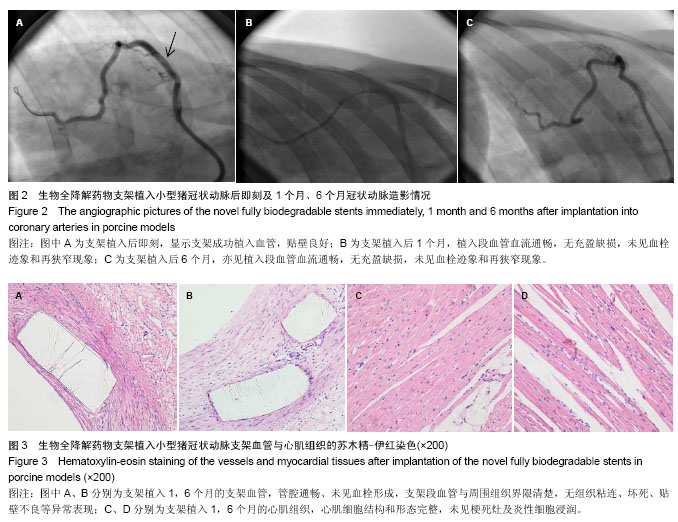
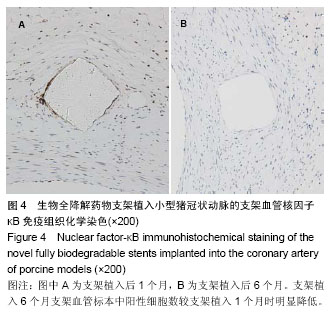
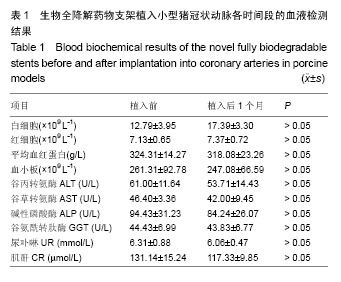
.jpg)
.jpg)